.jpg)
Gambia
CULTURAL HERITAGE OF THE GAMBIA
The cultural heritage of The Gambia is a rich tapestry woven from centuries of history, tradition, spirituality, and communal values. Despite being Africa’s smallest mainland country, The Gambia possesses a deeply rooted cultural identity shaped by indigenous African civilizations, Islamic scholarship, oral traditions, and historical encounters with Europe. Gambian culture emphasizes community, respect for elders, storytelling, music, and spiritual continuity, all of which continue to define the nation’s social fabric today.
Ethnic Diversity and Social Harmony
The Gambia is home to several ethnic groups, including the Mandinka, Fula (Fulani), Wolof, Jola, Serer, Manjago, and Sarahule, among others. Each group contributes distinct customs, languages, dress, and social structures, yet there is a strong tradition of peaceful coexistence and intermarriage. This cultural harmony has long been one of The Gambia’s defining strengths. Ethnic identity is respected, but national unity and communal cooperation take precedence over division.
Oral Tradition and Storytelling
One of the most important elements of Gambian cultural heritage is the oral tradition, preserved and transmitted by griots (jeli). Griots are historians, poets, musicians, and custodians of collective memory. Through songs, praise poetry, and storytelling, they preserve genealogies, moral teachings, historical events, and spiritual wisdom. This oral system predates written history and remains a vital educational and cultural institution in Gambian society.
Music, Dance, and Instruments
Music and dance are central to Gambian life and spiritual expression. Traditional rhythms accompany ceremonies such as naming rituals, weddings, harvest celebrations, and initiation rites. Instruments like the kora (a 21-string harp-lute), balafon, djembe, and sabar drums are not merely musical tools but sacred carriers of ancestral energy. Gambian music reflects themes of praise, social commentary, healing, and communal bonding.
Spiritual and Religious Heritage
Islam plays a dominant role in Gambian cultural life, with the majority of the population practicing Islam. Islamic scholarship, Quranic education, and Sufi traditions have flourished for centuries, particularly through ancient trade routes and learned clerical families. At the same time, indigenous African spiritual beliefs such as reverence for ancestors, sacred forests, and spiritual protection remain subtly integrated into daily life. This blending of Islamic faith and traditional spirituality creates a unique religious harmony that emphasizes morality, humility, and community responsibility.
Traditional Leadership and Social Values
Traditional governance structures, including village elders, alkalo (village heads), and councils, continue to play important roles alongside modern political systems. Respect for elders, communal decision-making, hospitality, and collective responsibility are foundational values. Greetings are elaborate and meaningful, reflecting social awareness and mutual respect. The extended family system remains strong, reinforcing solidarity and shared accountability.
Dress, Craft, and Material Culture
Traditional Gambian dress, such as boubous, kaftans, and embroidered garments, reflects cultural pride and spiritual dignity. Local crafts include weaving, pottery, leatherwork, wood carving, and tie-dye textiles. These crafts are not only economic activities but also cultural expressions passed down through generations, often infused with symbolic meanings and ancestral motifs.
Historical Legacy and Cultural Memory
The Gambia’s cultural heritage is also shaped by its historical role in trans-Saharan trade and later encounters with European powers during the colonial era. Sites such as Kunta Kinteh Island stand as powerful reminders of the transatlantic slave trade and the resilience of African identity. This history has fostered a strong sense of cultural memory, resistance, and global African connection.
Conclusion
The cultural heritage of The Gambia is a living tradition—rooted in ancestry yet adaptable to modern life. It is expressed through language, music, spirituality, social customs, and collective memory. Above all, Gambian culture emphasizes human dignity, unity, and continuity. In preserving and honoring its heritage, The Gambia maintains a strong cultural soul that continues to guide its people through change, challenge, and renewal.

Independence Day - April 27th 1961
GAMBIA
The Gambia, a small country in West Africa, is bordered by Senegal, except for its western coast on the Atlantic Ocean. Its narrow geography stretches along the Gambia River, which flows through the center of the country, giving it a unique and elongated shape. The Gambia covers an area of about 10,689 square kilometers, making it one of the smallest countries in mainland Africa.
The history of The Gambia is rich and varied, with evidence of human settlement dating back thousands of years. The region was part of the Mali and Songhai Empires during the medieval period, both of which were powerful and influential in West Africa. The Gambia became a significant location for trade, particularly in gold and slaves, attracting European interest. The Portuguese were the first Europeans to reach the Gambia River in the 15th century, followed by the British and French. In the 18th century, the British established control over the Gambia River and its surrounding areas, turning it into a British colony in 1889.
The Gambia gained independence from Britain on February 18, 1965, becoming a sovereign state within the Commonwealth. Dawda Jawara became the country's first Prime Minister and later its first President when The Gambia became a republic in 1970. Jawara's regime was marked by relative stability until 1994, when a military coup led by Yahya Jammeh overthrew the government. Jammeh ruled The Gambia for 22 years with an iron fist, during which human rights abuses were rampant. In December 2016, Adama Barrow won the presidential election, ending Jammeh's long rule and ushering in a new era of democracy.
The Gambia is a culturally diverse country with a population of about 2.4 million people. The official language is English, a legacy of its colonial past, but several indigenous languages are widely spoken, including Mandinka, Wolof, and Fula. These languages reflect the ethnic diversity of the country, which includes the Mandinka, Fula, Wolof, Jola, and Serahule people, among others.
The lifestyle in The Gambia varies between urban and rural areas. In the capital city, Banjul, and other urban centers like Serekunda, life is more modern, with access to amenities such as electricity, running water, and internet. Rural areas are more traditional, with many people engaged in subsistence farming and fishing. Extended family units are common, and social life is deeply intertwined with communal and family activities.
Gambian culture is vibrant and is expressed through music, dance, and festivals. The kora, a traditional stringed instrument, is central to Gambian music, and griots (traditional storytellers and musicians) play an important role in preserving the country's oral history. Islam is the predominant religion, practiced by over 90% of the population, and it influences many aspects of daily life, including food, dress, and holidays.
The political system of The Gambia is a presidential republic. The President, who is elected by popular vote, serves as both the head of state and government. The National Assembly is the legislative body, consisting of members elected every five years. The judiciary is independent, though it has faced challenges, especially during Jammeh's regime.
The Gambian economy is primarily based on agriculture, tourism, and remittances. Peanuts (groundnuts) are the main cash crop and a significant export. Tourism is a major industry, with visitors attracted to the country's beaches and wildlife. However, the economy faces challenges, including limited natural resources, a high unemployment rate, and a reliance on foreign aid and remittances from Gambians living abroad.
The Gambia is a country with a rich history, cultural diversity, and significant potential for development. Despite facing numerous challenges, particularly under prolonged authoritarian rule, the country is moving towards a more democratic and prosperous future. Its unique geography, vibrant culture, and resilient people make it a noteworthy nation in West Africa.
REFERENCE:
- [Gambia on Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Gambia)
- [Gambia: History, Geography, and Culture](https://www.britannica.com/place/The-Gambia)
- [CIA World Factbook: The Gambia](https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/gambia-the/)
THE ASTROLOGICAL ANALYSIS
OF THE GAMBIAN NATION
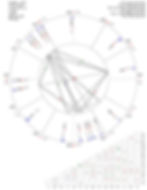
Astrology teaches that nations, like individuals, are born under specific cosmic conditions that shape their destiny, character, strengths, and vulnerabilities. A national horoscope reveals the psychological soul of a country, its karmic inheritance, leadership patterns, collective consciousness, and relationship with the wider world. The horoscope of The Gambia presents a deeply complex and symbolically rich chart that reflects resilience, hidden strength, internal tension, and a strong karmic link to leadership struggles and foreign involvement.
THE ASCENDANT AND NATIONAL IDENTITY
Gambia’s horoscope rises with Scorpio on the Ascendant, a sign associated with intensity, survival, secrecy, power struggles, and transformation. This immediately indicates that the nation’s identity is forged through deep trials, emotional endurance, and repeated cycles of crisis and rebirth. Scorpio rising nations are rarely passive; they endure pressure and often experience periods of domination, control, or suppression before eventual transformation. The ruler of Scorpio, Mars, is found in Virgo, closely conjunct the Moon. This placement reveals a people who are hardworking, service-oriented, analytical, and deeply sensitive to social conditions. Mars–Moon conjunctions often indicate a population that reacts emotionally to authority and governance. There is a strong link between survival instincts (Mars) and collective feelings (Moon), which explains why political decisions in The Gambia quickly affect public morale and social stability.
Mars and the Moon in Virgo also reflect a nation that compensates for lack of natural resources with human capital. Virgo is the sign of skill, training, service, education, and technical competence. Although The Gambia does not possess abundant mineral or natural wealth, it has historically attracted expertise, teachers, and institutional support from neighboring countries. Its educational sector, in particular, has served as a tool for nurturing, developing, and sustaining its citizenry.
PLANETARY CONCENTRATION AND LATENT POWER
In addition to Mars and the Moon, Pluto and Uranus are also located in Virgo, forming a powerful planetary cluster. Pluto represents deep transformation, control, and hidden power, while Uranus symbolizes sudden change, rebellion, and disruption. Their presence in Virgo suggests that the country undergoes profound internal changes through crises linked to systems, governance, labor, and public service. This concentration of planets gives The Gambia latent power disproportionate to its size. Though geographically small and narrow, the chart reveals enormous psychological and strategic energy that places the nation on equal footing with other African states in terms of influence and resilience. The struggle, however, lies in managing this power constructively rather than allowing it to erupt through instability.
Adding to this complexity is Neptune in the First House, a placement that strongly affects national self-image. Neptune here brings spiritual sensitivity, idealism, and compassion, but also confusion, deception, and lack of clarity about identity. This placement often manifests as unclear national direction, misplaced trust in leaders, and vulnerability to illusion—both internal and external.
COMPLEX PLANETARY PATTERNS AND KARMIC STRUCTURE
A striking feature of The Gambian horoscope is the presence of multiple advanced planetary configurations. These include:
A Double T-Square
A Grand Trine
A Wedge Pattern
A Talent Triangle
A Bow and Arrow Formation
Such configurations indicate a nation under strong karmic pressure but also endowed with exceptional potential.
The Double T-Square, rooted in the First, Fourth, and Seventh Houses, reflects tension between national identity (First House), domestic foundations and homeland security (Fourth House), and foreign relations (Seventh House). This pattern describes recurring conflicts between internal needs and external influences, often manifesting as political instability, leadership crises, or foreign interference in domestic affairs.
The quincunx and opposition aspects between the Virgo cluster (Moon, Mars, Pluto, Uranus) and the Aquarius planets (Sun, Mercury, Venus) intensify this struggle. Virgo seeks order, practicality, and service, while Aquarius emphasizes ideology, reform, and collective ideals. This mismatch creates friction between governance ideals and practical execution.
Additionally, Uranus in Virgo opposing Saturn in Pisces in the Fourth House symbolizes tension between sudden change and rigid foundations. Saturn in Pisces weakens structural authority, suggesting fragile national roots and emotional uncertainty around homeland security, land ownership, and traditional authority.
THE BOW AND ARROW SYMBOLISM
One of the most fascinating features of the chart is the Bow and Arrow pattern. In this configuration, Neptune in the First House forms the bow, while Jupiter in the Seventh House represents the arrow. Neptune, connected to the bow through sextiles and squares, symbolizes spiritual vision and collective ideals, while Jupiter, connected through trines and squares, represents expansion, foreign aid, diplomacy, and international support. This configuration suggests that The Gambia has an instinctive ability to sense opportunities, align with powerful allies, and strike at the right moment particularly in foreign relations. However, Neptune’s involvement also warns of miss-judgment and illusion. If the arrow is released without clarity or integrity, opportunities may be wasted or lead to dependency rather than empowerment.
THE OFFICE OF THE PRESIDENCY
In national astrology, the presidency is represented by the Tenth House and the Sun. In The Gambian horoscope, the Tenth House is ruled by Leo, making the Sun the significator of executive power. The Sun is located in Aquarius, a sign of collective ideals, reform, and rebellion but also the sign of the Sun’s detriment. This weakens centralized authority and makes leadership vulnerable to internal opposition, ideological division, and public mistrust. The Sun square Neptune in the First House is especially critical. This aspect reflects confusion, deception, and lack of transparency in leadership. It suggests presidents who may possess genuine intentions for reform but struggle with clarity, strategic planning, and public trust. This square also explains the recurring theme of betrayal, both perceived and real between the people and those in power. From independence through the present leadership era, this aspect has manifested as weak institutional planning, inconsistent governance strategies, and difficulty sustaining long-term national vision.
YAHYA JAMMEH AND KARMIC ALIGNMENT
The rule of Yahya Jammeh marked a significant chapter in The Gambia’s astrological story. His period in power coincided with certain planetary activations that temporarily stabilized the nation’s inherent tensions. Jammeh’s horoscope reportedly shares strong affinities with the national chart, granting him unusual control and longevity in office. During his regime, some infrastructural and administrative progress occurred, yet it came at the cost of brutal repression, fear, and human rights violations. This mirrors the darker expressions of Scorpio rising, Pluto dominance, and Mars–Moon conjunctions control through force and emotional manipulation. Like other African military rulers, like Jerry Rawlings, Idi Amin, Charles Taylor, Mobutu Sese Seko, Eyadema, and Sani Abacha, and Jammeh embodied the archetype of the authoritarian leader empowered temporarily by karmic alignment. However, astrology teaches that no transit lasts forever. When the cosmic tides shifted, his grip on power dissolved subtly but decisively.
THE BLESSINGS OF FOREIGN SUPPORT AND EDUCATIONAL GUIDANCE
The Seventh House, governing foreign relations and international partnerships, is strongly emphasized through Jupiter’s placement. Jupiter in the Seventh House, especially as part of a Grand Trine, is a powerful blessing. It reflects sustained foreign assistance, diplomatic goodwill, and educational guidance from international allies.
This Grand Trine links:
Jupiter in the Seventh House
Mars and Moon in Virgo from the Eleventh House of allies and networks
Lilith in Capricorn in the Third House of education, communication, and neighbouring environments
Although the planets occupy different elements, the pattern operates through air-house symbolism, emphasizing ideas, education, diplomacy, and strategic communication. This explains why The Gambia has benefited significantly from foreign scholarships, educational exchange programs, NGOs, and regional cooperation.
The Talent Triangle further suggests that the nation possesses untapped intellectual and strategic abilities, especially among its youth. When properly nurtured, these talents can transform national limitations into strengths.
CONCLUSION
The astrological chart of The Gambia reveals a nation of profound depth, karmic complexity, and unrealized potential. While plagued by internal tension, leadership struggles, and identity confusion, it is also blessed with strategic awareness, foreign support, and human capital. The future of The Gambia lies in conscious alignment, clarifying national vision, strengthening institutions, and transforming emotional insecurities into collective wisdom. Astrology does not predict fate; it reveals patterns. How those patterns are lived determines destiny.